FreeRADIUS Configuration Guide for Secure Authentication
Embark on a journey through the FreeRADIUS Configuration Guide for Secure Authentication, delving into the intricacies of network security and authentication. This guide aims to equip you with the knowledge and tools needed to ensure secure access within your network environment.
Introduction to FreeRADIUS Configuration

Secure authentication is a critical aspect of network environments, ensuring that only authorized users can access sensitive information and resources. FreeRADIUS plays a key role in network security by providing a centralized authentication and authorization service. Configuring FreeRADIUS properly can enhance the security of your network infrastructure and protect against unauthorized access.
Role of FreeRADIUS in Network Security
FreeRADIUS is an open-source, high-performance RADIUS server that is widely used for authenticating users and devices in a network. It acts as a centralized authentication server, allowing network administrators to control access to resources based on user credentials. By configuring FreeRADIUS, organizations can enforce strong authentication mechanisms and ensure that only authorized users can connect to the network.
Benefits of Configuring FreeRADIUS for Secure Authentication
- Enhanced Security: FreeRADIUS provides support for a variety of authentication protocols, such as EAP-TLS and PEAP, which offer more secure authentication methods than traditional password-based systems.
- Centralized Management: By configuring FreeRADIUS, organizations can centralize user authentication, simplifying the management of user accounts and access control policies.
- Scalability: FreeRADIUS is highly scalable and can handle a large number of authentication requests, making it suitable for networks of all sizes.
- Integration with Existing Systems: FreeRADIUS can be integrated with existing network infrastructure, such as LDAP or Active Directory, allowing organizations to leverage their existing user databases for authentication.
Setting Up FreeRADIUS Server
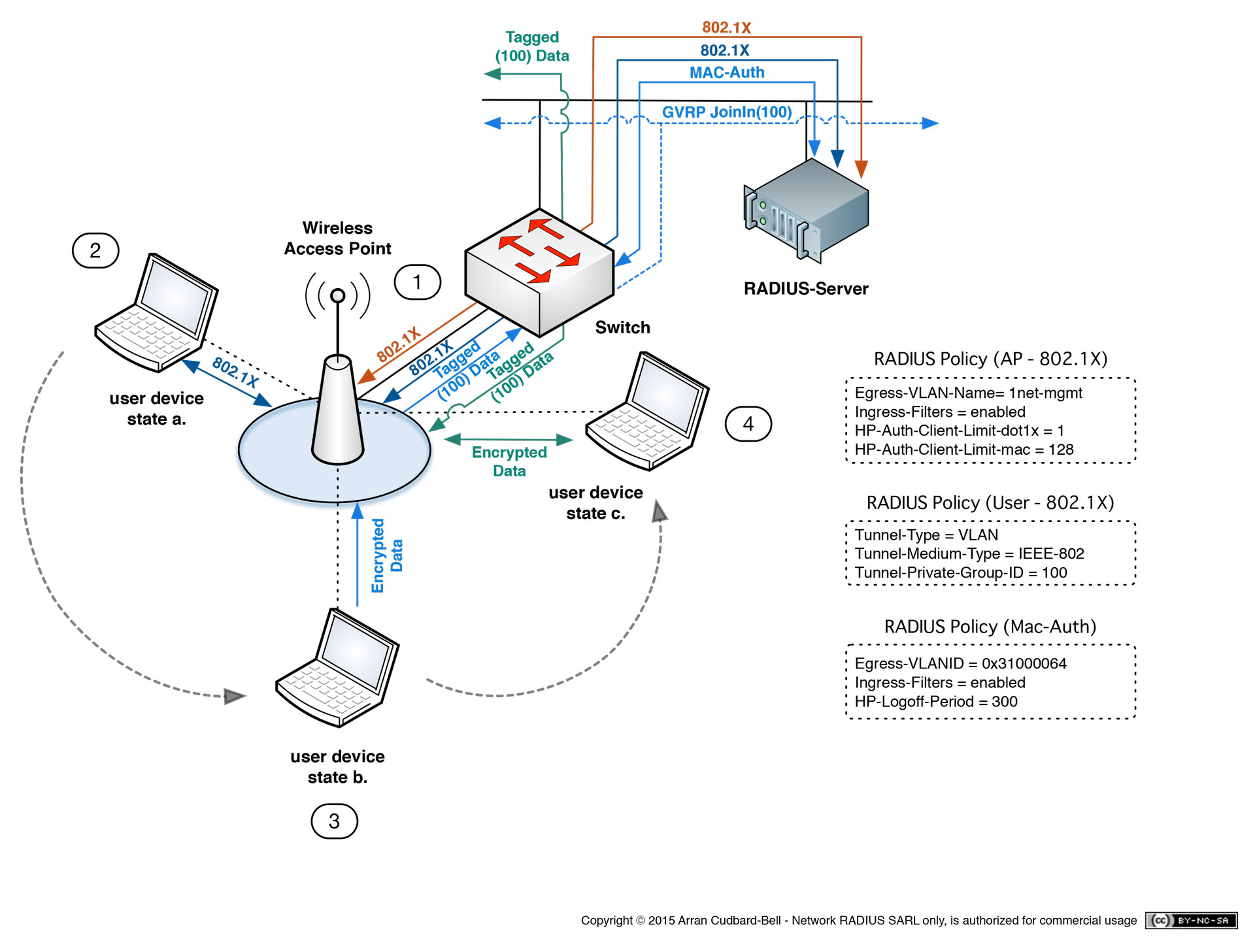
To set up a FreeRADIUS server, you will need to follow a series of steps to ensure proper installation and configuration. Below is a guide on how to install FreeRADIUS on different operating systems, configure basic server settings, and troubleshoot common pitfalls.
Installing FreeRADIUS on Different Operating Systems
- For Debian/Ubuntu: Use the command "sudo apt-get install freeradius" to install FreeRADIUS.
- For CentOS/RHEL: Execute the command "sudo yum install freeradius" to install FreeRADIUS.
- For macOS: Install FreeRADIUS using Homebrew with the command "brew install freeradius-server".
Basic Server Configuration Settings
- Configure the radiusd.conf file to set basic parameters like authentication ports and log file locations.
- Set up clients.conf to define the clients that can access the FreeRADIUS server.
- Edit users file to add user credentials for authentication.
Common Pitfalls and Troubleshooting
- Issue: Authentication failures. Troubleshoot by checking user credentials and ensuring correct configurations in users file.
- Issue: Server not starting. Check logs for errors, ensure correct permissions on configuration files, and restart the server.
- Issue: Unable to connect to the server. Verify network connectivity, firewall rules, and client configurations.
Configuring Users and Authentication Methods
When setting up FreeRADIUS for secure authentication, configuring users and selecting appropriate authentication methods are crucial steps to ensure the system's integrity and reliability.
Adding Users to FreeRADIUS
Before users can authenticate using FreeRADIUS, they need to be added to the system. This involves creating user profiles with unique credentials and permissions.
- Create a user profile in the FreeRADIUS users file by specifying a username and password.
- Assign attributes and access control rules to the user profile to define the level of access and privileges.
- Ensure that user credentials are stored securely and encrypted to prevent unauthorized access.
Authentication Methods in FreeRADIUS
FreeRADIUS supports various authentication methods, each offering different levels of security and compatibility with different network configurations.
- EAP-TLS:Uses certificates for mutual authentication, providing a high level of security.
- PEAP:Encapsulates EAP methods within a secure tunnel, offering protection against eavesdropping.
- TTLS:Combines the benefits of TLS with tunneled authentication for enhanced security.
- MD5:Basic authentication method using a shared secret between the client and server.
Securing User Credentials
Securing user credentials within FreeRADIUS configurations is essential to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Use strong encryption methods to store passwords securely, such as SHA-256 or bcrypt.
- Avoid storing plaintext passwords and instead use hashed or encrypted formats to protect sensitive information.
- Regularly update user passwords and enforce password complexity requirements to enhance security.
- Implement multi-factor authentication methods to add an extra layer of security for user authentication.
Implementing Security Measures
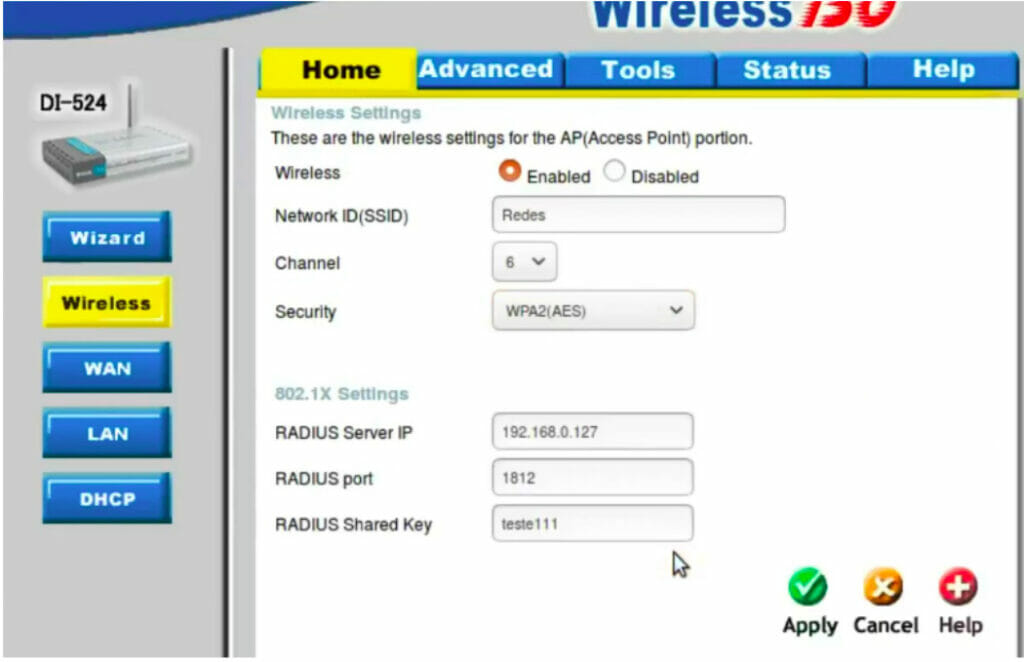
When it comes to securing your FreeRADIUS configuration, there are several key measures you can implement to enhance the overall security of your authentication system. This includes configuring SSL/TLS certificates for secure communication, adjusting firewall settings, and setting up access controls to protect against potential threats.
Configuring SSL/TLS Certificates
One of the essential steps in securing your FreeRADIUS server is configuring SSL/TLS certificates for encrypted communication. This will ensure that data exchanged between the RADIUS server and clients is secure and protected from unauthorized access. To set up SSL/TLS certificates, you will need to generate a certificate signing request (CSR), obtain a certificate from a trusted Certificate Authority (CA), and configure your FreeRADIUS server to use the certificate for secure communication.
Firewall Settings and Access Controls
Another crucial aspect of securing FreeRADIUS is configuring firewall settings and access controls to restrict unauthorized access to the server. By setting up firewall rules and access controls, you can regulate incoming and outgoing traffic to and from the RADIUS server, thereby reducing the risk of potential security breaches.
Make sure to only allow necessary ports and protocols for RADIUS communication and block any unwanted traffic that could pose a security threat.
Protecting Against DoS Attacks
Denial of Service (DoS) attacks can disrupt the normal operation of your FreeRADIUS server by overwhelming it with a high volume of traffic. To protect your server against DoS attacks, you can implement rate-limiting measures to control the number of authentication requests that can be processed within a specific timeframe.
Additionally, you can monitor server logs for any suspicious activity and configure intrusion detection systems to detect and mitigate potential threats before they escalate.
Integration with LDAP or Active Directory
Integrating FreeRADIUS with LDAP or Active Directory allows for centralized user management, making it easier to manage authentication and access control for large user bases.
Advantages of Integration
- Centralized User Management: LDAP or Active Directory integration centralizes user authentication and access control, simplifying administration tasks.
- Single Sign-On (SSO): Users can access multiple services with one set of credentials, enhancing user experience and security.
- Scalability: Easily scale user authentication and authorization as your organization grows without the need for manual user management.
Troubleshooting Tips
- Check Configuration Settings: Ensure that the FreeRADIUS server is configured with the correct LDAP or Active Directory settings, including server address, bind credentials, and search base.
- Test Connectivity: Verify network connectivity between the FreeRADIUS server and the LDAP or Active Directory server to ensure communication is established.
- Review Logs: Check FreeRADIUS logs for any error messages related to LDAP or Active Directory integration to identify and troubleshoot issues.
- Authentication Errors: If users are unable to authenticate, verify user credentials in LDAP or Active Directory and check for any account lockouts or password expiration issues.
Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, the FreeRADIUS Configuration Guide for Secure Authentication offers a comprehensive approach to fortifying your network against potential threats. By implementing the best practices Artikeld in this guide, you can enhance the security of your authentication processes and safeguard sensitive information effectively.