FreeRADIUS Advanced Configuration for Enhanced Network Authentication
Delving into the realm of FreeRADIUS Advanced Configuration for Enhanced Network Authentication opens up a world of possibilities for bolstering network security and authentication. From understanding the importance of advanced configuration to exploring various authentication methods, this topic promises to be both informative and engaging.
Overview of FreeRADIUS Advanced Configuration
Advanced configuration plays a crucial role in network authentication as it allows for fine-tuning security measures and customizing authentication processes to meet specific needs. FreeRADIUS, an open-source RADIUS server, offers advanced configuration options that enhance network security by implementing features such as multi-factor authentication, dynamic VLAN assignment, and policy-based access control.
Importance of Advanced Configuration in Network Authentication
Advanced configuration in network authentication is essential to strengthen security measures and ensure that only authorized users gain access to network resources. By configuring advanced settings in FreeRADIUS, administrators can implement additional layers of protection, such as certificate-based authentication, to prevent unauthorized access and safeguard sensitive data.
Role of FreeRADIUS in Enhancing Network Security
FreeRADIUS acts as a central authentication server that verifies the identity of users and devices attempting to connect to a network. With advanced configuration options, FreeRADIUS can enforce strict authentication policies, monitor and log authentication attempts, and integrate with external systems for enhanced security measures.
This ensures that only legitimate users are granted access to network resources, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and potential security breaches.
Scenarios Where Advanced Configuration is Necessary
- Implementing multi-factor authentication to add an extra layer of security beyond passwords.
- Configuring dynamic VLAN assignment based on user roles to restrict network access to specific resources.
- Enforcing policy-based access control to regulate user permissions and restrict unauthorized activities.
- Integrating FreeRADIUS with external databases for centralized user management and authentication.
Setting Up FreeRADIUS for Advanced Configuration
To set up FreeRADIUS for advanced configuration, you will need to follow a series of steps to install the software, modify specific configuration files, and implement best practices for securing FreeRADIUS during setup.
Step-by-Step Installation of FreeRADIUS
- Begin by installing FreeRADIUS using your package manager. For example, on Ubuntu, you can use the command:
sudo apt-get install freeradius
- Once installed, start the FreeRADIUS service by running:
sudo service freeradius start
- Verify that FreeRADIUS is running correctly by checking the status:
sudo service freeradius status
Configuration Files for Advanced Settings
- One of the key configuration files to modify for advanced settings is
radiusd.conf, which contains general settings for the FreeRADIUS server. - Additionally, you may need to modify
clients.confto define the clients that are allowed to connect to the FreeRADIUS server. - For more advanced configurations, you can explore files like
usersfor user authentication settings andpolicy.conffor policy definitions.
Best Practices for Securing FreeRADIUS
- Ensure that you regularly update FreeRADIUS to the latest version to patch any security vulnerabilities.
- Implement strong passwords for the FreeRADIUS administrator account and for clients connecting to the server.
- Enable logging and monitoring to track any suspicious activity or unauthorized access attempts.
- Consider setting up firewalls to restrict access to the FreeRADIUS server from unauthorized sources.
Advanced Authentication Methods in FreeRADIUS
Authentication methods play a crucial role in securing network access, and FreeRADIUS offers a variety of advanced options to enhance network authentication. Let's explore the different authentication methods supported by FreeRADIUS and how they can be configured for specific network requirements.
EAP-TLS
EAP-TLS (Extensible Authentication Protocol-Transport Layer Security) is a strong authentication method that requires both the server and the client to present digital certificates for mutual authentication. This method ensures a high level of security by encrypting the entire authentication process.
EAP-TTLS
EAP-TTLS (Extensible Authentication Protocol-Tunneled Transport Layer Security) is another authentication method that provides a secure tunnel for authentication. Unlike EAP-TLS, EAP-TTLS only requires the server to present a certificate, while the client can authenticate using credentials such as a username and password within the secured tunnel.
PEAP
PEAP (Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol) is similar to EAP-TTLS in that it creates a secure tunnel for authentication. However, PEAP is specifically designed to address potential vulnerabilities in EAP-TTLS, making it a preferred choice for many organizations. PEAP also supports various inner authentication methods, providing flexibility in deployment.
Configuring Advanced Authentication Methods
To configure advanced authentication methods in FreeRADIUS, you need to modify the configuration files to specify the desired authentication protocols, certificates, and other parameters. Each method has its own configuration settings, which can be customized based on the security requirements and network environment.
By carefully configuring these methods, you can ensure a robust and secure authentication process for your network.
Implementing Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) with FreeRADIUS

Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is a security model that restricts system access based on the roles assigned to individual users. Each user is assigned a specific role with predetermined permissions, allowing them access to only the resources necessary to perform their job functions.
RBAC helps organizations manage access control efficiently, reduce the risk of unauthorized access, and enhance overall network security.
Implementation of RBAC in FreeRADIUS
- Define Roles: Start by defining different roles within your organization, such as admin, user, guest, etc. Each role should have specific permissions and access levels.
- Assign Roles: Once roles are defined, assign them to individual users based on their job responsibilities and access requirements.
- Configure Policies: Use FreeRADIUS configuration files to set up policies that enforce role-based access control. These policies determine what resources each role can access.
- Integration with LDAP: Integrate FreeRADIUS with LDAP or Active Directory to centralize user authentication and role assignments.
Advantages of RBAC for Access Control
- Granular Access Control: RBAC allows organizations to assign precise permissions to users, ensuring they only have access to the resources necessary for their roles.
- Reduced Risk: By limiting access based on roles, RBAC reduces the risk of unauthorized users gaining entry to sensitive data or systems.
- Simplified Management: RBAC makes access control management easier by streamlining the assignment and revocation of user permissions.
- Scalability: RBAC can easily scale with the organization as new users and roles are added, providing a flexible and efficient access control solution.
Closing Summary
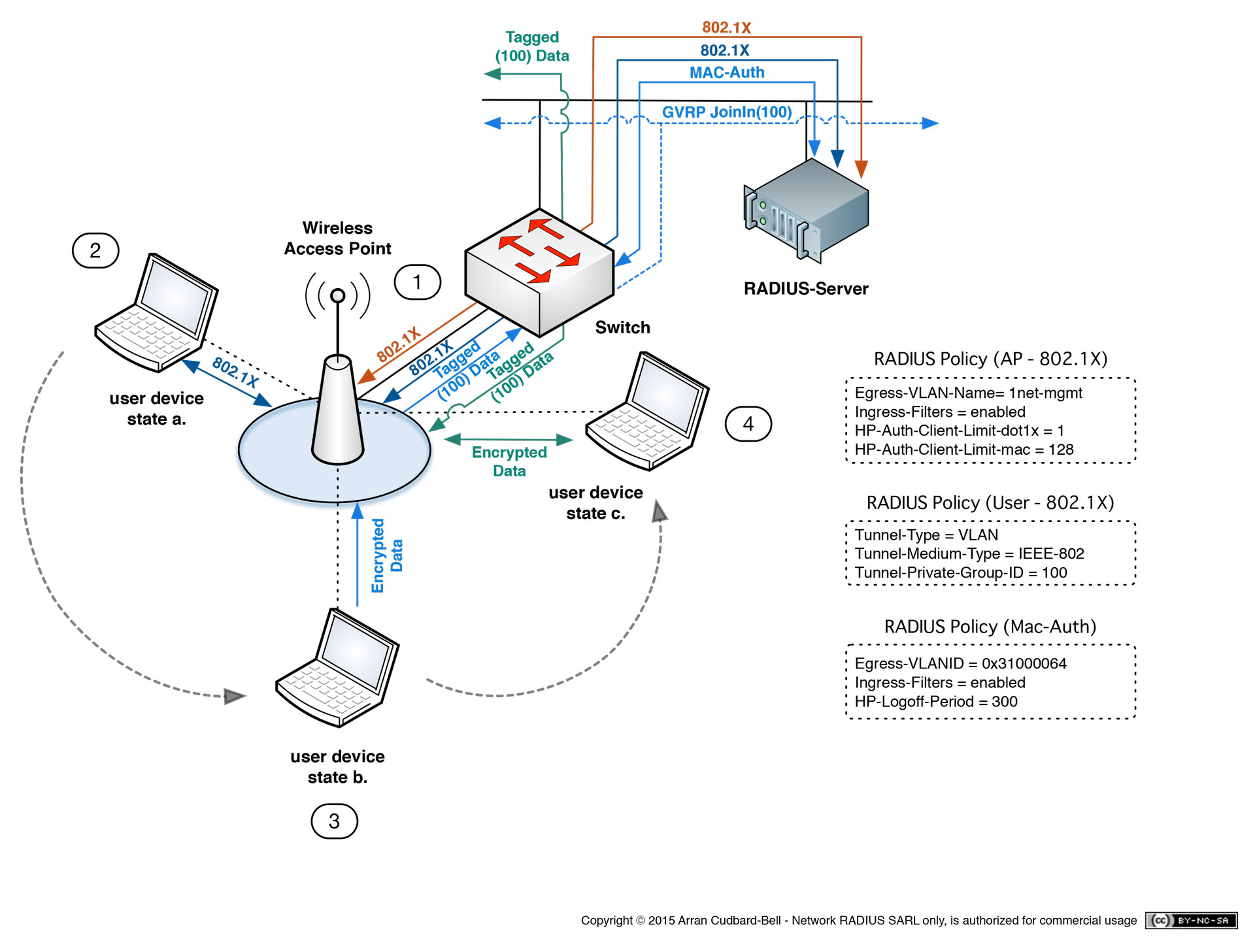
In conclusion, FreeRADIUS Advanced Configuration equips network administrators with the tools and knowledge needed to ensure robust network security through enhanced authentication methods. By implementing role-based access control and leveraging advanced authentication techniques, organizations can fortify their networks against potential threats.