Comparative Analysis: Edge Server Versus Traditional Cloud Solutions sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset.
As we delve into the intricacies of edge servers and traditional cloud solutions, a world of possibilities opens up to explore the nuances that shape modern data management strategies.
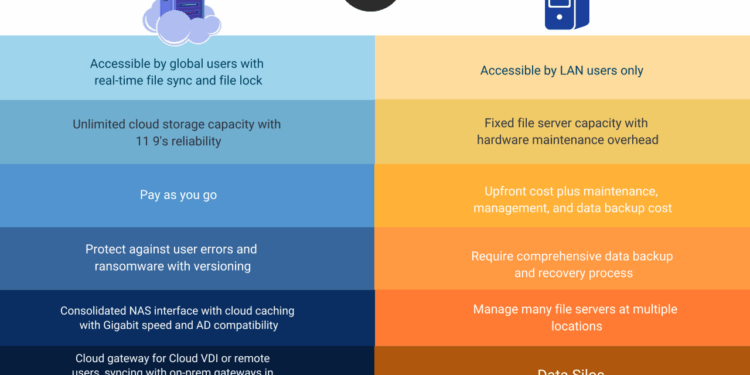
Edge Server Overview
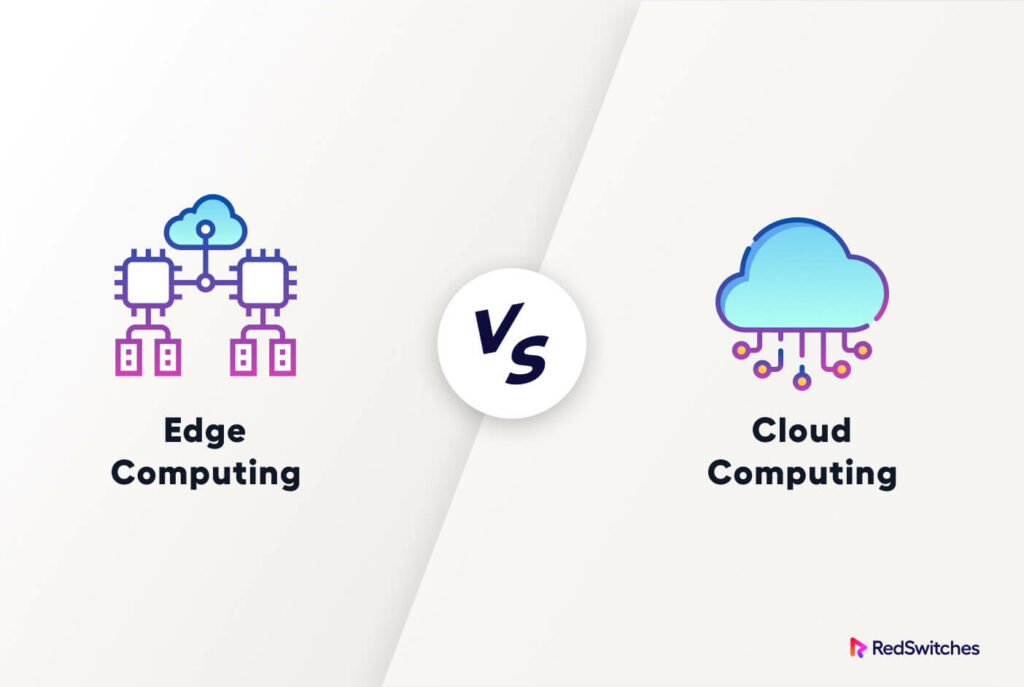
An edge server is a type of server that is located closer to the end-users, typically at the edge of the network. This positioning allows the edge server to process data and deliver content faster by reducing latency. Unlike traditional cloud solutions where data is stored and processed in centralized data centers, edge servers bring computing resources closer to where they are needed.
Differences from Traditional Cloud Solutions
- Edge servers reduce latency: By processing data closer to the end-users, edge servers minimize the time it takes for information to travel back and forth, resulting in faster response times.
- Improved performance: Edge servers can enhance performance for applications that require real-time data processing, such as IoT devices or online gaming.
- Increased data privacy and security: Since data is processed locally on the edge server, sensitive information can be kept closer to the source, reducing the risk of data breaches.
Scenarios where Edge Servers are Preferred
- IoT devices: Edge servers are ideal for IoT applications where real-time data processing is crucial, such as smart home devices or industrial sensors.
- Content delivery networks (CDNs): Edge servers are commonly used in CDNs to cache content closer to end-users, improving load times for websites and streaming services.
- Remote locations: In areas with limited connectivity to centralized data centers, edge servers can provide faster access to data and applications.
Performance and Latency
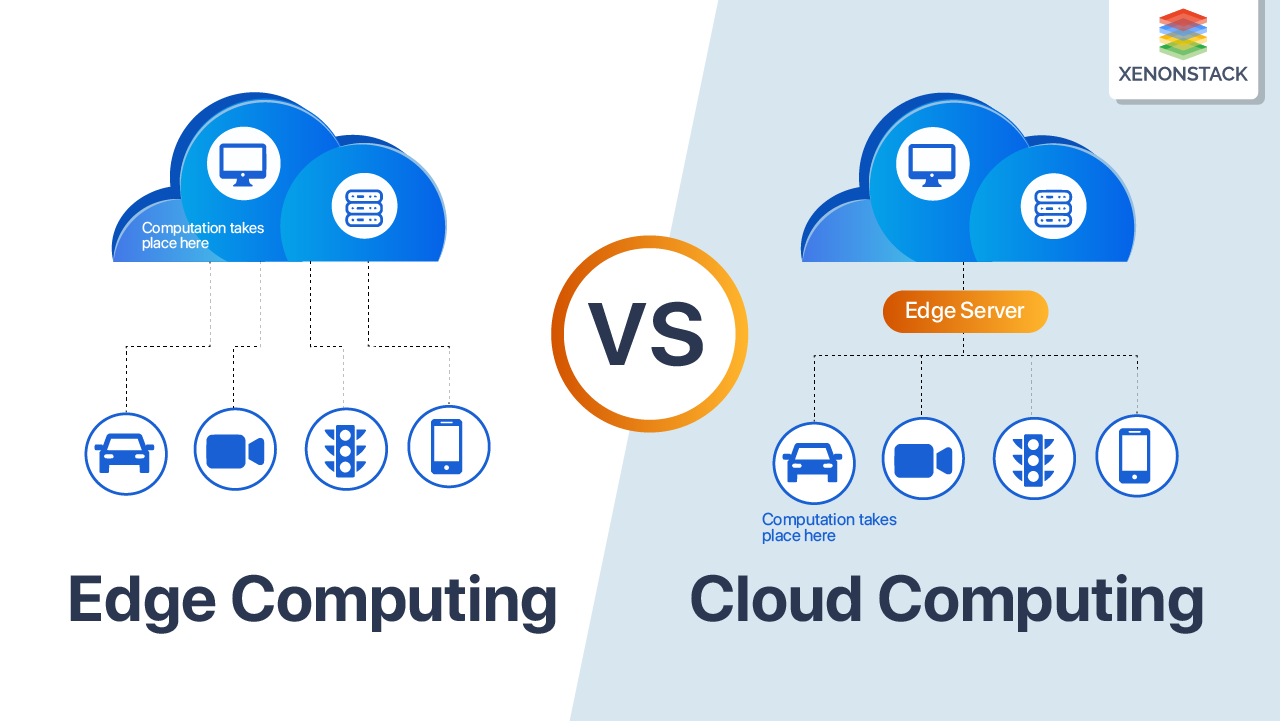
Edge servers play a crucial role in enhancing performance and reducing latency in data transmission compared to traditional cloud solutions. By bringing computing power closer to the end user, edge servers help optimize data processing and delivery, resulting in faster response times and improved user experience.
Impact on Performance
- Edge servers significantly reduce the distance data needs to travel, leading to faster processing and response times.
- With edge computing, tasks that require real-time processing can be executed more efficiently, enhancing overall system performance.
- By offloading data processing tasks from centralized cloud servers to edge nodes, performance bottlenecks can be minimized.
Reducing Latency in Data Transmission
- Edge servers help minimize latency by processing data closer to the end user, reducing the time it takes for information to travel back and forth.
- By caching content at the edge, frequently accessed data can be delivered quickly without the need to retrieve it from distant cloud servers.
- Real-time applications, such as video streaming or online gaming, benefit greatly from reduced latency provided by edge servers.
Real-World Examples
- Netflix utilizes edge servers to cache popular content at local points of presence, ensuring faster streaming speeds for users worldwide.
- Tesla leverages edge computing to process data from its fleet of vehicles in real-time, enabling features like Autopilot and over-the-air updates.
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers AWS Outposts, bringing cloud services to on-premises locations for low-latency data processing and storage.
Scalability and Flexibility
When comparing edge servers with traditional cloud solutions, scalability and flexibility play a crucial role in determining the efficiency and adaptability of the system. Edge servers offer unique advantages in terms of scalability and flexibility, enabling businesses to optimize resource allocation and meet dynamic demands effectively.Edge servers provide enhanced scalability compared to traditional cloud solutions by distributing computing resources closer to the end-users.
This proximity allows for faster data processing and reduced latency, especially for applications requiring real-time interactions. The ability to scale resources at the edge enables businesses to handle sudden spikes in traffic without compromising performance, ensuring seamless user experiences even during peak periods.In addition to scalability, edge servers offer greater flexibility in resource allocation by allowing organizations to customize computing capabilities based on specific needs and requirements.
Unlike traditional cloud solutions, which often follow a one-size-fits-all approach, edge servers empower businesses to allocate resources strategically according to workload demands, application requirements, and user locations. This dynamic resource allocation ensures optimal performance and cost-efficiency, as resources are utilized efficiently without unnecessary overspending.
Use Cases of Edge Server Flexibility
- Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): Edge servers are widely used in CDNs to cache and deliver content closer to end-users, reducing latency and improving load times. By dynamically allocating resources based on user location and content popularity, CDNs can optimize content delivery and ensure a seamless user experience.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Applications: Edge servers play a critical role in IoT applications by processing data locally at the edge, minimizing latency and enhancing real-time decision-making. The flexibility of edge servers allows IoT devices to offload processing tasks to the edge, ensuring efficient resource utilization and responsiveness.
- Mobile Edge Computing (MEC): Edge servers are essential in MEC environments, where low latency and high bandwidth are crucial for mobile applications. By dynamically scaling computing resources at the edge, MEC platforms can deliver high-performance services to mobile users while optimizing network efficiency and reducing operational costs.
Security Features
Edge servers offer enhanced security features compared to traditional cloud solutions, providing organizations with increased protection for their data and privacy. By processing data closer to the source, edge servers reduce the risk of data breaches during transmission to centralized cloud servers.
This proximity also enables real-time data processing and analysis, enhancing security measures.
Enhanced Data Encryption
Edge servers utilize advanced encryption techniques to secure data both in transit and at rest. This ensures that sensitive information remains protected throughout the data processing and storage phases. By encrypting data at the edge, organizations can mitigate the risk of unauthorized access and maintain data integrity.
Local Data Processing
One key security advantage of edge servers is the ability to process data locally, reducing the need to transfer sensitive information to external servers. This localized approach minimizes the exposure of data to potential security threats during transmission. Industries such as healthcare, finance, and government agencies greatly benefit from this enhanced security measure, as they deal with highly confidential data that requires maximum protection.
Improved Compliance Measures
Edge servers enable organizations to adhere to strict data privacy regulations and compliance standards by storing and processing data within specified geographic regions. This ensures that data residency requirements are met, reducing the risk of non-compliance penalties. Industries that handle personal or sensitive data, such as healthcare and finance, find this feature crucial in maintaining regulatory compliance and safeguarding customer information.
Conclusive Thoughts
In conclusion, the comparison between edge servers and traditional cloud solutions sheds light on the evolving landscape of data infrastructure, highlighting the diverse approaches available to businesses seeking optimal performance, security, and scalability.