Edge Server vs Cloud Server: Key Differences & Benefits sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality.
In this article, we delve into the distinctions between Edge Servers and Cloud Servers, exploring their functionalities, architectures, data processing methods, latency handling, and security measures.
Define Edge Server and Cloud Server
An Edge Server is a type of server that is located closer to the end-users to reduce latency and improve performance by processing data locally. On the other hand, a Cloud Server is a remote server that offers various services over the internet, allowing users to access and store data in a centralized location.
Differentiate between Edge Server and Cloud Server
- Edge Server functions by processing data closer to the end-users, reducing latency, while Cloud Server operates remotely over the internet.
- Edge Server is ideal for applications that require real-time processing and low latency, such as IoT devices and content delivery networks, while Cloud Server is suitable for storing large amounts of data and running complex applications.
- Companies in industries like gaming, healthcare, and finance typically use Edge Servers to deliver content quickly and efficiently, while companies in industries like e-commerce and software development rely on Cloud Servers for data storage and processing.
Architecture and Infrastructure
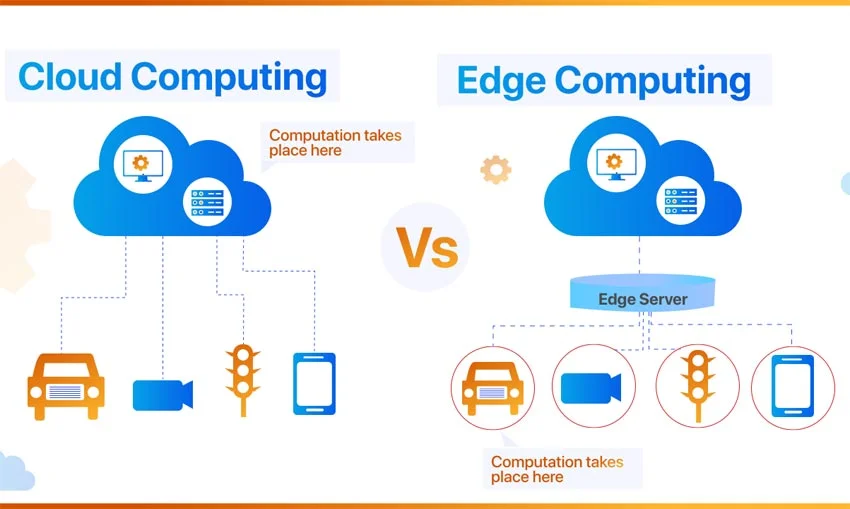
When it comes to architecture and infrastructure, both Edge Servers and Cloud Servers play crucial roles in delivering services efficiently. Let's delve into the specifics of each to understand their unique characteristics and capabilities.
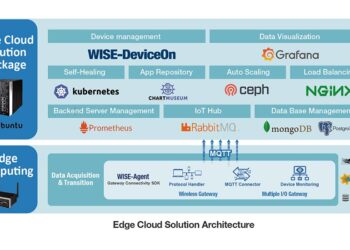
Edge Server Architecture and Infrastructure
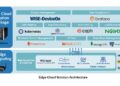
An Edge Server is typically located closer to the end-user, at the edge of the network, hence the name. This proximity allows for faster access to content and reduced latency. The architecture of an Edge Server includes multiple servers distributed geographically to serve content locally.
It caches data to reduce the load on the origin server, improving response times for users. Edge Servers are designed to handle high volumes of traffic efficiently, making them ideal for content delivery networks (CDNs) and applications that require low latency.
Cloud Server Architecture and Infrastructure
On the other hand, Cloud Servers operate in a centralized data center or multiple data centers across regions. They rely on virtualization technology to create virtual instances that can be scaled up or down based on demand. Cloud Servers offer flexibility, scalability, and redundancy, allowing for seamless resource allocation and efficient management of workloads.
These servers are connected through a network of data centers, providing high availability and reliability for users.
Comparison of Architecture and Infrastructure
- Scalability:
Edge Servers are limited in scalability due to their distributed nature, while Cloud Servers can easily scale resources up or down based on demand.
- Reliability:
Cloud Servers offer higher reliability with redundant systems and data centers, ensuring continuous operation even in case of failures. Edge Servers may face challenges in terms of reliability due to their distributed architecture.
- Performance:
Edge Servers provide faster access to content and lower latency for end-users due to their proximity, whereas Cloud Servers offer consistent performance and resource allocation across a network of data centers.
Data Processing and Storage
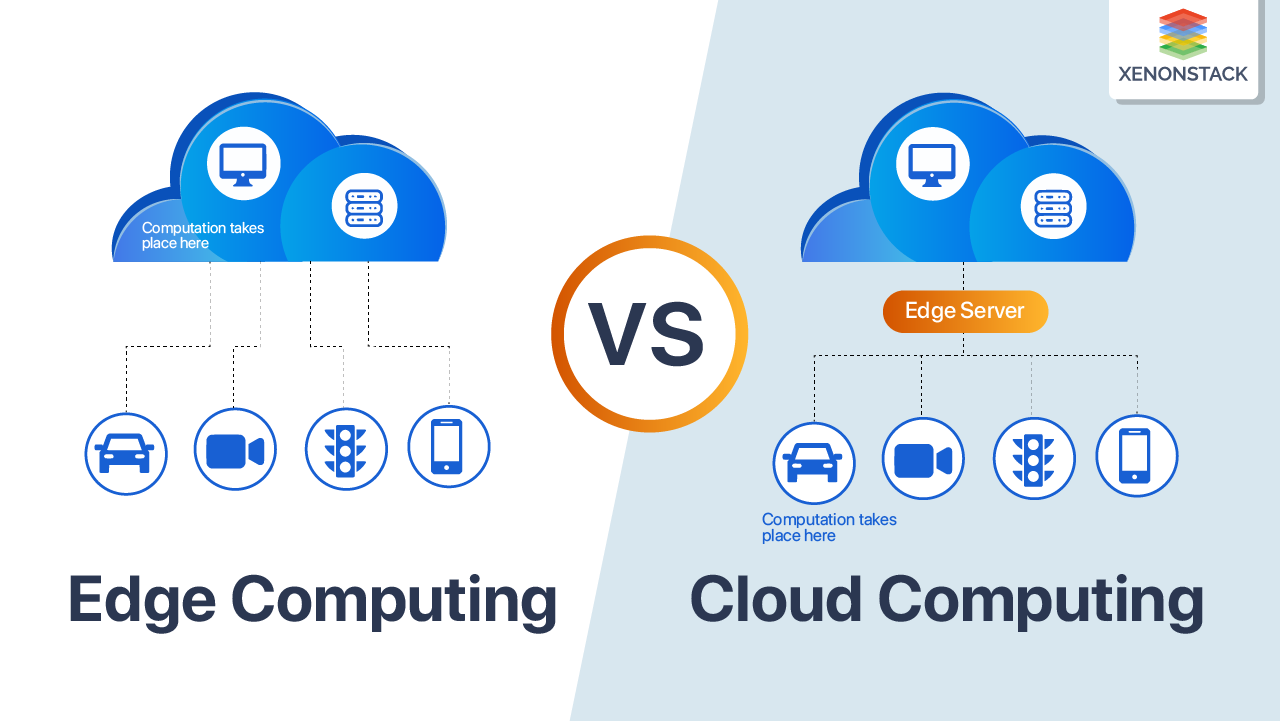
When it comes to data processing and storage, both Edge Servers and Cloud Servers play crucial roles in managing information efficiently. Let's delve into how data processing is handled in each type of server and compare their data storage capabilities.
Data Processing in Edge Servers
Edge Servers are designed to process data closer to the source, reducing latency and improving response times. These servers analyze and filter data locally before sending relevant information to the Cloud. This real-time processing at the edge enables faster decision-making and enhances overall system performance.
Data Processing in Cloud Servers
Cloud Servers, on the other hand, handle data processing in centralized data centers. They are equipped with powerful computing resources and storage capacities to process large volumes of data. Cloud Servers are ideal for complex computations, big data analytics, and applications that require extensive processing capabilities.
Data Storage Capabilities
- Edge Servers: Edge Servers are limited in terms of storage capacity due to their compact size and focus on processing data locally. They typically store only essential data needed for immediate processing or quick access.
- Cloud Servers: Cloud Servers offer virtually unlimited storage capacity, allowing organizations to store massive amounts of data securely in the Cloud. This scalability makes Cloud Servers ideal for storing vast datasets, backups, and archives.
Latency and Speed
When it comes to Edge Servers and Cloud Servers, the issue of latency and speed plays a crucial role in determining the efficiency and effectiveness of data processing. Let's delve into how these servers handle latency and speed differently to meet the demands of users.
Edge Servers: Reducing Latency
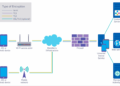
Edge Servers are strategically placed closer to the end-users, typically at the edge of the network, to reduce the distance data needs to travel. By processing data locally, closer to where it is generated, Edge Servers help minimize latency significantly.
This proximity allows for faster response times and improved user experience, especially for applications that require real-time data processing.
Cloud Servers: Managing Latency and Speed
On the other hand, Cloud Servers operate from centralized data centers, which may be located farther away from end-users compared to Edge Servers. While Cloud Servers may experience higher latency due to the longer distance data must travel, they compensate by offering scalable resources and robust infrastructure.
Cloud Servers manage latency by optimizing network connections, utilizing content delivery networks (CDNs), and implementing caching mechanisms to enhance speed and responsiveness.
Impact on User Experience
Latency and speed directly impact user experience on both Edge Servers and Cloud Servers. For Edge Servers, the reduced latency results in faster data processing, quicker response times, and seamless interactions for users. This is particularly beneficial for applications like video streaming, online gaming, and IoT devices that demand low latency.
On the other hand, Cloud Servers prioritize scalability and resource availability, ensuring consistent performance and reliability across a wide range of applications. While users may experience slightly higher latency with Cloud Servers, the robust infrastructure and optimization techniques help maintain satisfactory speed levels for most operations.
Security Measures
When it comes to data security, both Edge Servers and Cloud Servers implement various measures to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access or cyber threats. Let's delve into the security features of each to understand how they differ and which one may be more suitable for specific use cases.
Security Measures in Edge Servers
Edge Servers typically focus on securing data at the edge of the network, closer to where it is being generated or consumed. Some common security measures implemented in Edge Servers include:
- Encryption of data in transit and at rest to prevent interception or unauthorized access.
- Firewalls and access control mechanisms to regulate traffic and ensure only authorized users can access the server.
- Regular security updates and patches to address vulnerabilities and protect against emerging threats.
- Physical security measures to safeguard hardware from theft or tampering.
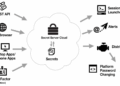
Security Measures in Cloud Servers
Cloud Servers, on the other hand, rely on a different set of security measures due to their centralized nature and remote accessibility. Some common security features implemented in Cloud Servers include:
- Multi-factor authentication to enhance user verification and prevent unauthorized access.
- Data encryption both in transit and at rest to maintain confidentiality and integrity of information.
- Regular security audits and compliance checks to ensure adherence to industry standards and regulations.
- Network monitoring and intrusion detection systems to detect and respond to security threats in real-time.
Comparison of Security Features
In comparing the security features of Edge Servers versus Cloud Servers, it is essential to consider the specific requirements of the workload and the level of control needed over data security. While Edge Servers provide proximity to data sources and faster processing, they may require additional security measures to protect data at the edge.
On the other hand, Cloud Servers offer scalability and centralized management but may pose higher risks due to the shared infrastructure and remote access. Ultimately, the choice between Edge Servers and Cloud Servers for security depends on factors such as data sensitivity, regulatory requirements, and the desired level of control over security measures.
Final Review
In conclusion, the comparison between Edge Servers and Cloud Servers reveals a nuanced understanding of their unique advantages and applications. This discussion sheds light on the dynamic landscape of server technology, emphasizing the importance of choosing the right solution based on specific needs and requirements.